TOPIC INFO (UGC NET)
TOPIC INFO – UGC NET (Geography)
SUB-TOPIC INFO – Geography of Environment (UNIT 4)
CONTENT TYPE – Detailed Notes
What’s Inside the Chapter? (After Subscription)
1. Introduction
2. Global Warming
2.1. Mechanism of Global Warming
2.2. Causes of Global Warming
2.3. Effects of Global Warming
2.4. Control Measure of Global Warming
3. Urban Heat Island
3.1. Causes of the Urban Heat Island Effect
3.2. Impact of the Urban Heat Island effect
3.3. Urban Heat Islands in India
3.4. Conclusion
4. Air Pollution
4.1. Types of Air Pollutants
4.2. Sources of Air Pollution
4.3. Effects of Air Pollutants
4.4. Fly Ash
4.5. Lead
4.6. Metallic Oxides
4.7. Nanoparticles (NPs)
4.8. Major Gaseous Air Pollutants. Their Sources & Effects
4.9. Control of Air Pollution
5. Water Pollution
5.1. Sources Of Water Pollution
5.2. Causes of Water Pollution
5.3. Effects of Water Pollution
5.4. Eutrophication
6. Land Degradation
6.1. Introduction to Land Degradation
6.2. Definition
6.3. Global Land Degradation
6.4. Causes of Land Degradation
6.5. Mechanisms that Initiate Land Degradation
6.6. Prevention Measures for Land Degradation
6.7. Control Measures for Land Degradation
6.8. Land Degradation Processes
6.9. Land Degradation and Productive
Note: The First Topic of Unit 1 is Free.
Access This Topic With Any Subscription Below:
- UGC NET Geography
- UGC NET Geography + Book Notes
Environmental Hazards and Disaster
UGC NET GEOGRAPHY
Geography of Environment (UNIT 4)
Introduction
- Environmental hazards are those extreme events caused by natural process or man’s activities which exceed the tolerable magnitude within or beyond certain time limits and make adjustments difficult and thus result in loss of property and lives, such as earthquakes, floods, volcanic eruptions etc.
- The World Commission on Environment and Development warned that the 1980s seemed destined to sweep the dire trend of catastrophic natural disasters into a crisis-filled 1990s. The problem has prompted the United Nations General Assembly to proclaim the International Decade for Natural Disaster Reducation which began on first January, 1990.
- WHO defines disaster as “any occurrence that causes damage, economic distraction, loss of human life and deterioration in health and health services on a scale sufficient to warrant an extraordinary response from outside the affected community or area.”
- Disaster can be a natural or man-made phenomenon. Any distortion in the balanced equation between earth’s resources, stock and ecology arising out of climatic changes, movement of the earth occurring inside and other natural process may lead to natural disaster like cyclone, floods, draughts, earthquakes, volcanoes, landslides, heat waves, and cold waves etc. Hazards arising out of man-made technological advancements, industrialisation and other developmental activities are coined as technological disasters like emission of deadly industrial pollutants, soil erosion and nuclear disaster etc.
- India is one of the most disaster prone countries with all sorts of hazards being visited in some parts of the country or the other every year. The natural hazards are related to climate, water and geological causes. Besides natural, the other hazards, as recognised by High Powered Committee on Disaster Management relate to chemical, Industrial, nuclear, biological and accidental disasters.
- Over the last two decades the natural disasters have claimed over three million lives and adversely affected 800 million people worldwide with 90 percent of the victims being from developing countries. In India, there are a total of 593 districts, of which 199 are most disaster prone.
Global Warming
- “Global warming is a gradual increase in the earth’s temperature generally due to the greenhouse effect caused by increased levels of carbon dioxide, CFCs, and other pollutants.”
- Global warming is the long-term heating of Earth’s climate system observed since the pre-industrial period (between 1850 and 1900) due to human activities, primarily fossil fuel burning, which increases heat-trapping greenhouse gas levels in Earth’s atmosphere. The term is frequently used interchangeably with the term climate change, though the latter refers to both human- and naturally produced warming and the effects it has on our planet. It is most commonly measured as the average increase in Earth’s global surface temperature.
- Global warming is the phenomenon of a gradual increase in the temperature near the Earth’s surface. This phenomenon has been observed over the past one or two centuries. This change has disturbed the climatic pattern of the earth. However, the concept of global warming is quite controversial but the scientists have provided relevant data in support of the fact that the temperature of the Earth is rising constantly.
- There are several causes of global warming, which have a negative effect on humans, plants and animals. These causes may be natural or might be the outcome of human activities. In order to curb the issues, it is very important to understand the negative impacts of global warming.
- In recent past, global observations have provided clear evidence of climatic changes resulting from anthropogenic activities. According to a report from World Watch Institute (1992), the earth’s surface was warmest in 1990. Six of seven warmest years on record have occurred since 1980.
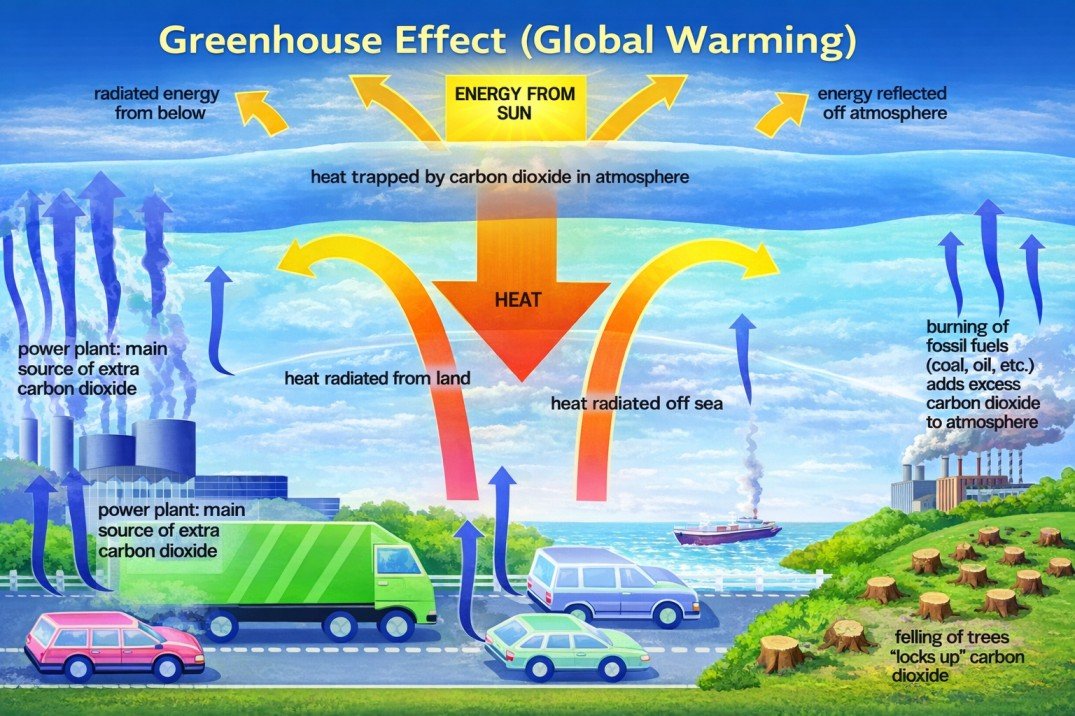
- Observations on temperature at many places of the world over the last century show an average increase of about 0.5° K This is supported by Palaeo-climatic evidence gathered from deep-sea ice-cores from Arctic and Antarctic regions. While the primary cause of an increase in global temperature in the past has been increasing concentration of CO2 fossil fuel burning, extensive deforestation, rapid increase in chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) has further complicated the global environmental problems.
- The minor gaseous constituents more commonly known as trace gases or greenhouse gases (GHGs) like CO2, Clox, CH4, N2O, NOX, O3 CFCs etc., though occur in traces but play a surprisingly dominant role in regulating the entire earth’s atmosphere.
Mechanism of Global Warming
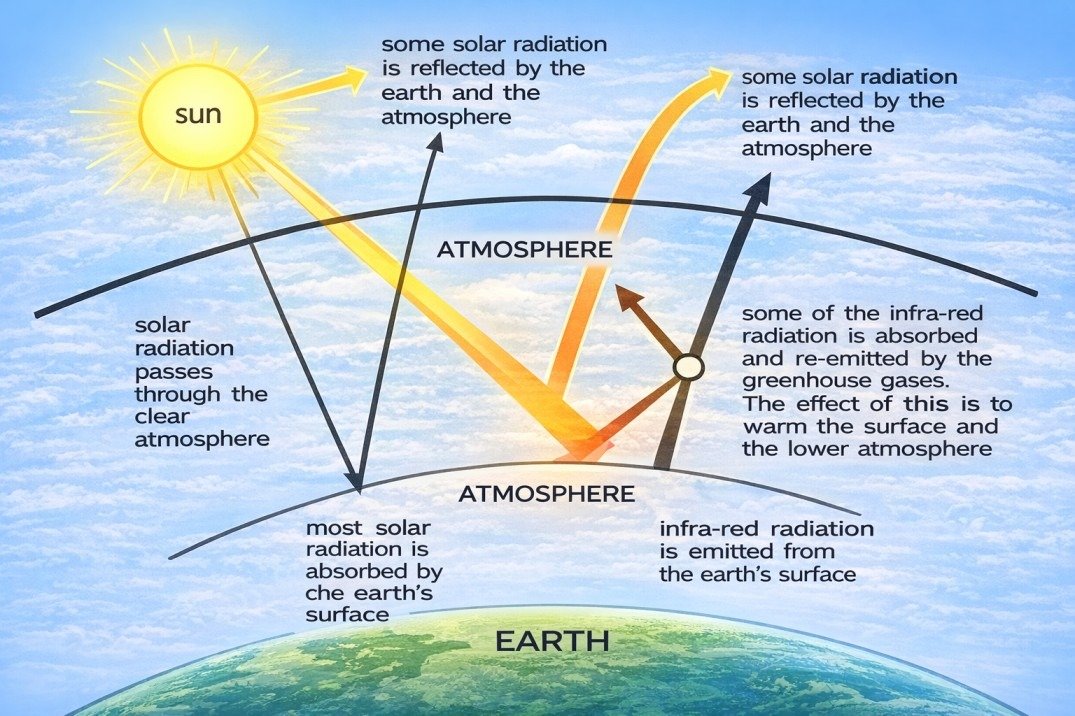
- The incoming radiation from the Sun is mostly in the form of visible light and nearby wavelengths, largely in the range 0.2 4 1m, corresponding to the Sun’s radiative temperature of 6,000 K. Almost half the radiation is in the form of “visible” light, which our eyes are adapted to use.
- About 50% of the Sun’s energy is absorbed at the earth’s surface and the rest is reflected or absorbed by the atmosphere. The reflection of light back into space – largely by clouds – does not much affect the basic mechanism; this light, effectively, is lost to the system.
- The absorbed energy warms the surface. Simple presentations of the greenhouse effect, such as the idealized greenhouse model, show this heat being lost as thermal radiation. The reality is more complex: the atmosphere near the surface is largely opaque to thermal radiation (with important exceptions for “window” bands), and most heat loss from the surface is by sensible heat and latent heat transport.
Radiative energy losses become increasingly important higher in the atmosphere largely because of the decreasing concentration of water vapour, an important greenhouse gas. It is more realistic to think of the greenhouse effect as applying to a “surface” in the mid-troposphere, which is effectively coupled to the surface by a lapse rate.
Causes of Global Warming
Following are the major causes of global warming:
Man-made Causes of Global Warming:
- Deforestation: Plants are the main source of oxygen. They take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen thereby maintaining environmental balance. The forests are being depleted for many domestic and commercial purposes. This has led to an environmental imbalance, thereby giving rise to global warming.
- Use of Vehicles: The use of vehicles even for a very short distance results into various gaseous emissions. Vehicles burn fossil fuels which emit a large amount of carbon dioxide and other toxins into the atmosphere resulting in a temperature increase.
- Chlorofluorocarbon: With the excessive use of air conditioners and refrigerators, humans have been adding CFCs into the environment which affects the atmospheric ozone layer. The ozone layer protects the earth surface from the harmful ultraviolet rays emitted by the sun. The CFCs has led to ozone layer depletion making way for the ultraviolet rays, thereby increasing the temperature of the earth.
- Industrial Development: With the advent of industrialization, the temperature of the earth has been increasing rapidly. The harmful emissions from the factories add to the increasing rom the facto temperature of the earth. In 2013, the Intergovernmental Panel for Climate Change reported that the increase in the global temperature between 1880 and 2012 has been 0.9 degrees Celsius. The increase is 1.1 degrees Celsius when compared to the pre-industrial mean temperature.
- Agriculture: Various farming activities produce carbon dioxide and methane gas. These add to the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere and increase the temperature of the earth.
- Overpopulation: Increase in population means more people breathing. This leads to an increase in the level of carbon dioxide, the primary gas causing global warming, in the atmosphere.
- Signs of Global Warming: The receding of ice formations on earth (snows at mountain-tops, glaciers, and Antarctic and Arctic ice). The increase of shrubbery in Arctic. Thinner clouds over the sky that decrease the ability to reflect heat from the sun. The discovery of the decrease of earth’s albedo (the amount of sunlight reflection by the earth surface to the moon) by 2.5 percent, which means the earth, has lost some levels of capability to reflect sunlight to the moon. Change in wind directions.
Natural Causes of Global Warming:
- Volcanoes: Volcanoes are one of the largest natural contributors to global warming. The ash and smoke emitted during volcanic eruptions goes out into the atmosphere and affects the climate.
- Water Vapour: Water vapour is a kind of greenhouse gas. Due to the increase in earth’s temperature more water gets evaporated from the water bodies and stays in the atmosphere adding to global warming.
- Melting Permafrost: Permafrost is there where Permafrost is there where glaciers are present. It is a frozen soil that has environmental gases trapped in it for several years. As the permafrost melts, it releases the gases back into the atmosphere increasing the earth’s temperature.
- Forest Blazes: Forest blazes or forest fires emit a large amount of carbon-containing smoke. These gases are released into the atmosphere and increase the earth’s temperature resulting in global warming.
Effects of Global Warming
Following are the major effects of global warming:
- Rise in Temperature: Global warming has led to an incredible increase in earth’s temperature. Since 1880, the earth’s temperature has increased by 1 degrees. This has resulted in an increase in the melting of glaciers, which have led to an increase in the sea level. This could have devastating effects on coastal regions. It is estimated that the earth’s mean temperature will rise between 1.5 to 5.5°C by 2050 if input of greenhouse gases continues to rise at the present rate. Even at the lower value, earth would be warmer than it has been for 10,000 years.
- Threats to the Ecosystem: Global Warming has affected the coral reefs that can lead to a loss of plant and animal lives. Increase in global temperatures has made the fragility of coral reefs even worse.
- Climate Change: Global warming has led to a change in climatic conditions. There are droughts at some places and floods at some. This climatic imbalance is the result of global warming.
- Spread of Diseases: Global warming leads to a change in the patterns of heat and humidity. This has led to the movement of mosquitoes that carry and spread diseases.
- High Mortality Rates: Due to an increase in floods, tsunamis and other natural calamities, the average death toll usually increases. Also, such events can bring about the spread of diseases that can hamper human life.
- Loss of Natural Habitat: A global shift in the climate leads to the loss of habitats of several plants and animals. In this case, the animals need to migrate from their natural habitat and many of them even become extinct. This is yet another major impact of global warming on biodiversity.
Rise in Sea Level:
- With the increase in global temperature sea water will expand. Heating will melt the polar ice sheets and glaciers resulting in further rise in sea level. Current models indicate that an increase in the average atmospheric temperature of 3°C would raise the average global sea level by 0.2-1.5 meters over the next 50-100 years.
- One meter rise in sea level will inundate low lying areas of cities like Shanghai, Cairo, Bangkok, Sydney, Hamburg and Venice as well as agricultural lowlands and deltas in Egypt, Bangladesh, India, China and will affect rice productivity.
- This will also disturb many commercially important spawning grounds, and would probably increase the frequency of storm damage to lagoons, estuaries and coral reefs. In India, the Lakshadweep Islands with a maximum height of 4 meters above the sea level may be vulnerable.
- Some of the most beautiful cities like Mumbai may be saved by heavy investment on embankment to prevent inundation. Life of millions of people will be affected by the sea level rises who have built homes in the deltas of the Ganges, the Nile, the Mekong, the Yangtze and the Mississippi rivers.
Effects on Human Health:
- The global warming will lead to changes in the rainfall pattern in many areas, thereby affecting the distribution of vector-borne diseases like malaria, filariasis, elephantiasis etc. Areas which are presently free from diseases like malaria; schistosomiasis etc. may become the breeding grounds for the vectors of such diseases.
- The areas likely to be affected in this manner are Ethiopia, Kenya and Indonesia. Warmer temperature and more water stagnation would favour the breeding of mosquitoes, snails and some insects, which are the vectors of such diseases. Higher temperature and humidity will increase/aggravate respiratory and skin diseases.
Effects on Agriculture:
- There are different views regarding the effect of global warming on agriculture. It may show positive or negative effects on various types of crops in different regions of the world. Tropical and subtropical regions will be more affected since the average temperature in these regions is already on the higher side.
- Even a rise of 2°C may be quite harmful to crops. Soil moisture will decrease and evapotranspiration will increase, which may drastically affect wheat and maize production. Increase in temperature and humidity will increase pest growth like the growth of vectors for various diseases.
- Pests will adapt to such changes better than the crops. To cope up with the changing situation, drought resistant, heat resistant and pest resistant varieties of crops have to be developed.
Control Measure of Global Warming
There are numerous ways to stop global warming:
- Plant More Trees and Stop Contributing to Deforestation: This is by far the easiest measure to save our planet from the hazards of global warming. Global warming can be attributed to the large scale concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. That being said planting trees can help in absorbing this harmful gas and help in regulating its amount in the atmosphere and help in preventing global warming by lessening green house effect.
- Switch to Compact Fluorescent Light Bulbs: Every household which uses incandescent bulbs contributes to global warming on a large scale. On the whole, these bulbs add 300 lbs of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere every year. Replacing incandescent bulbs with energy saving Compact Fluorescent Light bulbs (CFLs) can help in reducing carbon dioxide generation and help you to save 60 per cent of energy.
- Reuse and Recycle Products: Reusing and recycling various products which we use in our day to day life can also help you in doing your bit to stop global warming. For instance, recycling paper will make sure that the large scale felling of trees to produce paper is stopped, and these trees will in turn absorb the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere and reduce global warming.
- Unplug Appliances: Unplugging appliances to save energy is yet another effective way to address the problems of global warming. Simply unplugging all the electronic devices which are not in use can help in saving 20 per cent energy. More importantly, importantly, it will also help in reducing your electricity bill by 10 per cent every month.
- Avoid Keeping Electrical Appliances on Standby: Similarly, keeping electronic appliances on standby also contributes to loss of energy and global warming, and therefore is best avoided. One may feel that keeping a single computer on standby won’t make a big difference, but when millions of people think in this manner it does make a drastic difference.
- Use a Programmable Thermostat: A thermostat helps in regulating the temperature by altering heat supply. Make sure that you keep your thermostat as low as possible during the winter, and as high as possible during the summer. Lowering the thermostat by 2 degrees in winter and increasing it by 2 degrees in summer can help in keeping 2,000 lbs of carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere.
- Promote the use of organic products: Promoting the use of organic foods is also one of the effective ways to prevent global warming. The tendency of organic soils to capture carbon dioxide far exceeds that of the soil used in conventional farming. Estimates suggest that we can get rid of 580 billion lbs of carbon dioxide if we resort to organic farming for food production.
- Use Vehicles Efficiently: One of the leading causes of pollution, vehicles dump a great amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. If we stop using vehicle we can cut down of great amount of pollution. If you can’t resist vehicle, you can opt to efficient driving tips, such as turning the engine off at red lights and driving at moderate speeds, and contribute in curbing global warming. Ideally though, you should opt for public transport or other environment friendly modes of transportation such as cycling.
- Resort to Alternative Sources of Energy: One of the most talked about global warming solution is to switch to alternative energy sources such as solar power and wind power. You can easily harness these sources of nature to generate power, and replace fossil fuels with it. Doing away with fossil fuels alone will help in reducing the huge amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere every day.
- Become a Responsible Citizen: This is the most important among the various measures to curb global warming. We need to acknowledge the fact that we are responsible for this menace to a great extent. Just implementing the simple steps to stop global warming mentioned above can make a huge difference. You can also come up with your own novel ways to contribute for this cause. For instance, one of our readers had made a valid point by saying, “If we sacrifice the unnecessary luxuries in our life, we can contribute in saving the tremendous amount of energy which goes in their production.” Resorting to these 10 ways to stop global warming can help us to curb the problem to a significant extent.
