TOPIC INFO (CUET PG)
TOPIC INFO – CUET PG (Political Science)
SUB-TOPIC INFO – International Relations
CONTENT TYPE – Short Notes
What’s Inside the Chapter? (After Subscription)
1. Extent of Cold War
2. Meaning/Definition
3. Nature of Cold War
4. Marshall Plan
5. Causes of Cold War
6. Factor Responsible for Cold War
6.1. Stalin
6.2. Truman Doctrine
6.3. Both US and USSR
7. Evolution of Cold War
7.1. Phase I (1946-62)
7.2. Phase II (1962-79)
7.3. Phase III: New Cold War (1979-89)
8. End of Cold War
9. Factors that Led to End of Cold War
9.1. Limitations of Communism
9.2. Impact of Gorbachev’s Reform
9.3. US Policy and ‘Second’ Cold War
9.4. Economic and Cultural Globalization
10. Conclusion
Access This Topic With Any Subscription Below:
- CUET PG Political Science
- CUET PG Political Science + Book Notes
Cold War politics
CUET PG
Political Science
- The end of World War II is a landmark episode in world history. Allied powers (led by USA, USSR, Britain and France) defeated the Axis Powers (led by Germany, Italy and Japan). After dropping of atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki, Japan surrendered. This led to end of one of the most devastating wars in world history. But this was the beginning of a new phase in the contemporary world history. The post-1945 world is characterized by the emergence of the USA and the USSR as ‘superpowers’.
- The superpower era and the associated rivalry between them, was characterized as the Cold War. Age-old antagonisms that had been buried during the war resurfaced leading to the phase of the Cold War. The period of Cold War was marked by tensions between an increasingly US-dominated West and a Sovietdominated East. The multi-polarity of the pre-World War II period thus gave way to Cold War bi-polarity.
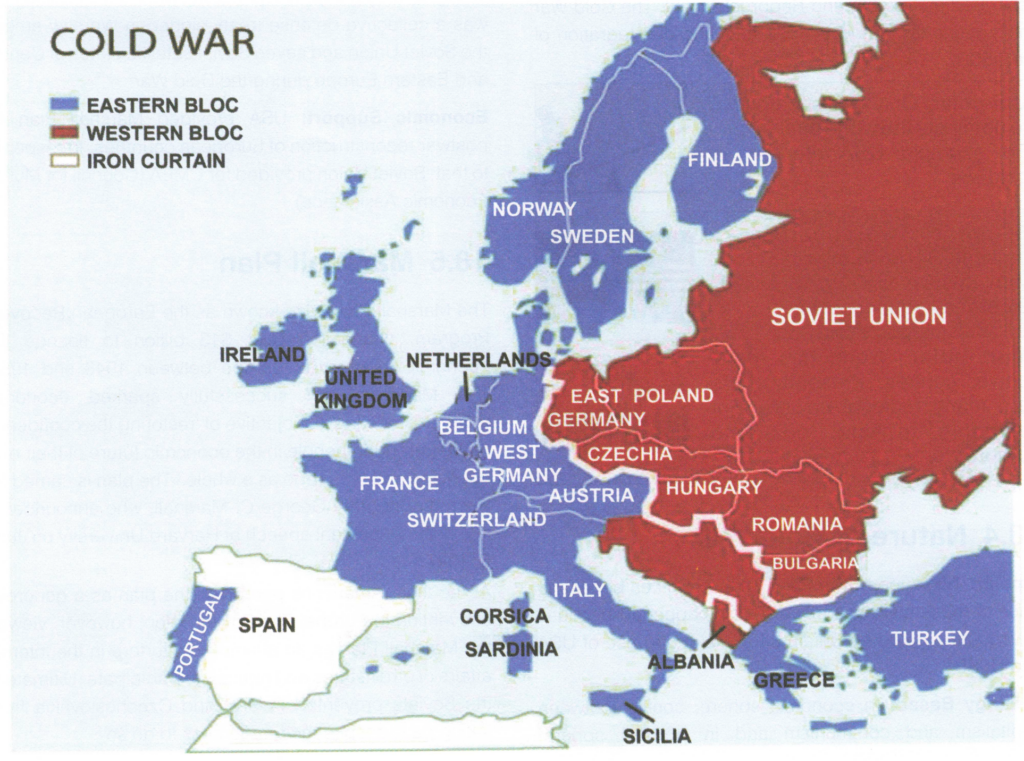
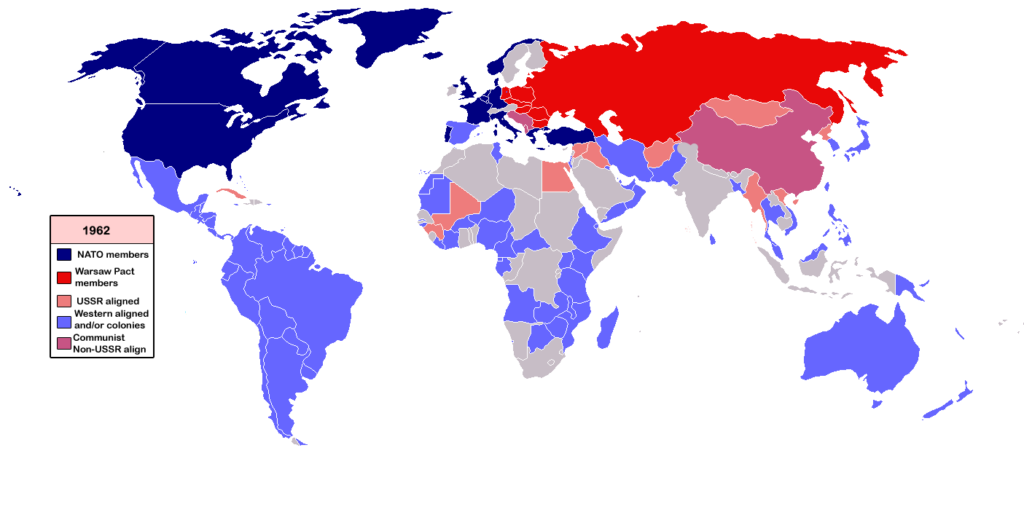
Extent of Cold War
- Eastern Bloc: It comprised of countries of Eastern Europe which were allies of USSR. They followed communism.
- Western Bloc: Countries of Western Europe and ally of USA. They pursued liberalism.
Meaning/Definition
- Cold war is the term used to describe the antagonistic relationship between the USA and the USSR after the Second World War till the end of the cold war in 1991.
- The war is called cold because there was no direct military confrontation between the two superpowers. All the wars fought were localized but involved indirect support from the two superpowers- the United States and the USSR.
- It means that both the superpowers would have come to direct confrontation, had circumstances allowed. The most hostile condition, when they almost came close to a war, was during the Cuban Missile Crisis in 1962.
- The United States and the USSR gradually strengthened their own zones of influence, dividing the world into two divided camps. It was not exclusively a struggle between the US and the USSR but a global conflict that affected many countries, particularly the continent of Europe.
- Indeed, Europe, divided into two blocs, became one of the main theatres of the war. In Western Europe, the European integration process began with the support of the United States, while the countries of Eastern Europe became satellite nations of the USSR.
- But the period is marked with warmer and cooler phases. There were covert operations like proxy wars and conflicts linked to East-West conflict (Korean Crisis, Vietnam War , Israeli-Arab War, etc.). This was the warmer phase.
- Whereas during cooler phase, we can observe that there was cooperation between the superpowers. This phase is described as Detente and Rapprochement. The Cold War finally came to an end in 1991 after the disintegration of the USSR.
PRACTICE QUESTIONS OF THIS TOPIC
1. Which of the following best explains why the Cold War is termed “cold”?
A) Because it occurred during winter months
B) Because there was no direct military confrontation between the USA and USSR
C) Because both nations signed a peace treaty
D) Because it involved only propaganda
2. What event marked the symbolic beginning of the Cold War era?
A) The Truman Doctrine
B) Winston Churchill’s Fulton Speech (Iron Curtain speech) in 1946
C) The formation of NATO
D) The Korean War
3. Which of the following statements best describes the bipolar nature of the Cold War?
A) Existence of multiple power centers
B) Emergence of several small states as superpowers
C) Dominance of two superpowers, the USA and the USSR, with their respective blocs
D) Equal distribution of power among UN members
4. Which of the following was a major ideological conflict during the Cold War?
A) Feudalism vs Capitalism
B) Imperialism vs Nationalism
C) Capitalism vs Communism
D) Liberalism vs Fascism
5. Which of the following best describes the Eastern Bloc?
A) Communist countries of Eastern Europe allied with the USSR
B) Liberal democratic countries of Western Europe
C) Non-aligned nations of Asia and Africa
D) Western European capitalist nations
