TOPIC INFO (UGC NET)
TOPIC INFO – UGC NET (Geography)
SUB-TOPIC INFO – Geography of Environment (UNIT 4)
CONTENT TYPE – Detailed Notes
What’s Inside the Chapter? (After Subscription)
Note: The First Topic of Unit 1 is Free.
Access This Topic With Any Subscription Below:
- UGC NET Geography
- UGC NET Geography + Book Notes
Human Interaction and Impacts
UGC NET GEOGRAPHY
Geography of Environment (UNIT 4)
Human Environmental Interactions can be defined as interactions between the human social system and (the “rest” of) the ecosystem. Human social systems and ecosystems are complex adaptive systems (Marten, 2001). Complex because ecosystems and human social systems have many parts and many connections between these parts. Adaptive because they have feedback structures that promote survival in a constantly changing environment.
Human social system
In order to analyse Human Environmental Interactions it is important to be aware of specific characteristics of the human social system. The type of society strongly influences peoples attitude towards nature, their behaviour and therefore their impact on ecosystems. Important characteristics of human social systems are population size, social organization, values, technology, wealth, education, knowledge and many more. Especially values and knowledge strongly influence peoples “view of life” and consequently define the way people act. The choice of possible actions is then limited by the available technology.
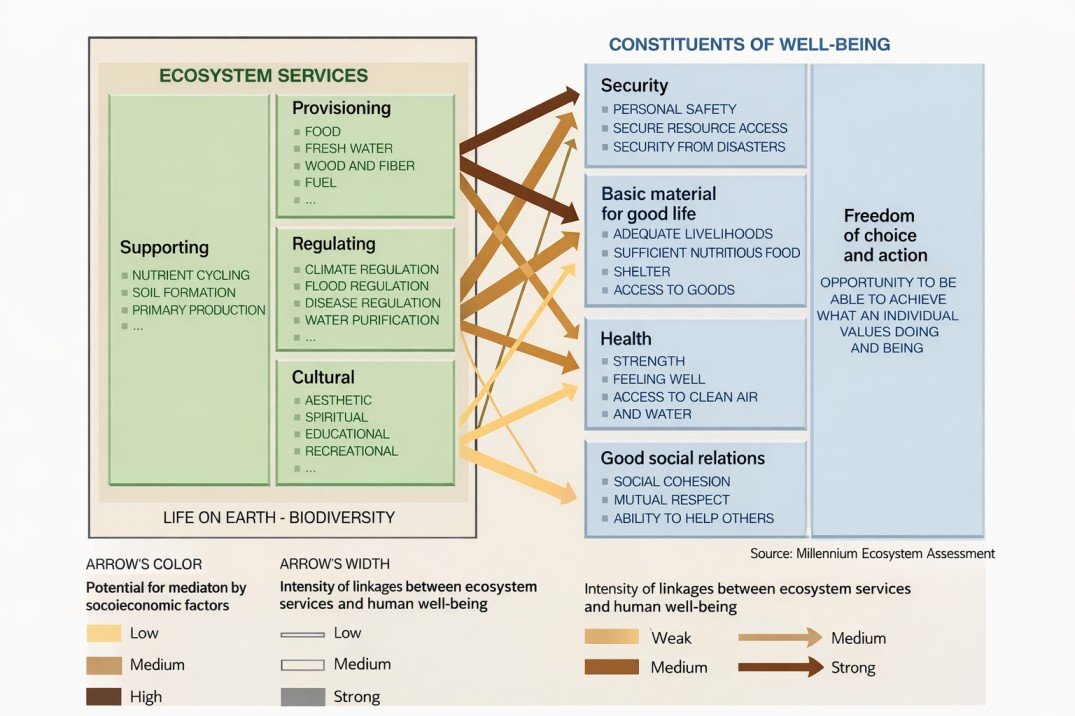
People modify the environment for their purposes and obtain benefits (Ecosystem Services) from it. These Ecosystem Services are essential for human well-being and include for example the provision of resources like water, timber, food, energy, information, land for farming and many more. Obviously by using these resources people affect the environment in a lot of ways. Furthermore people often reorganize existing ecosystems to achieve new ones that seem to be more effective in serving their needs.
The Millenium Ecosystem Assessment (MA) analysed how Ecosystem Services and constituents of human well-being are interlinked. The MA research programme was launched with support from the United Nations in 2001.